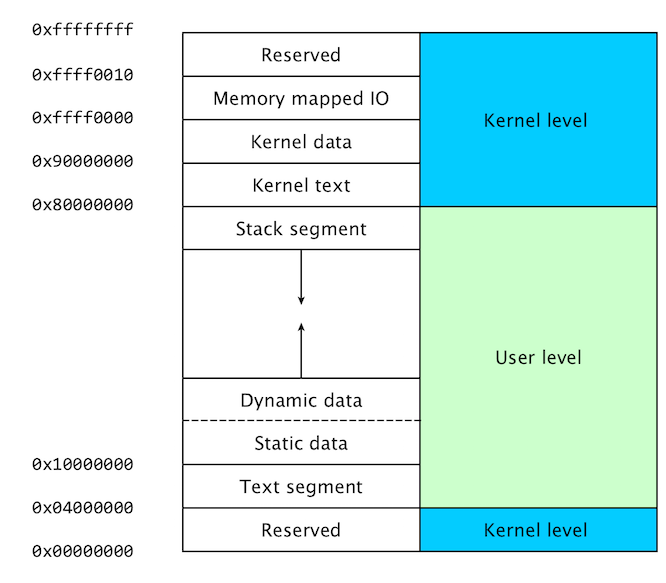
Mips memory layout
To execute a MIPS program memory must be allocated. The MIPS computer can
address 4 Gbyte of memory, from address 0x0000 0000 to 0xffff ffff. User memory
is limited to locations below 0x7fff ffff. In the below figure the layout of the
memory allocated to a MIPS program is shown.
The purpose of the various memory segments:
- The user level code is stored in the text segment.
- Static data (data known at compile time) use by the user program is stored in the data segment.
- Dynamic data (data allocated during runtime) by the user program is stored in the heap.
- The stack is used by the user program to store temporary data during for example subroutine calls.
- Kernel level code (exception and interrupt handlers) are stored in the kernel text segment.
- Static data used by the kernel is stored in the kernel data segment.
- Memory mapped registers for IO devices are stored in the memory mapped IO segment.