Initial definitions
CPU
The central processing unit (CPU) is the electronic circuitry within a computer that carries out the instructions of a computer program by performing the basic arithmetic, logical, control and input/output (I/O) operations specified by the instructions. 1
Register
A processor register is a quickly accessible location available to a computer’s central processing unit (CPU). Registers usually consist of a small amount of fast storage. 2 A CPU only has a small number of registers.
Memory
Memory refers to the computer hardware integrated circuits that store information for immediate use in a computer; it is synonymous with the term “primary storage”. 3 The memory is much slower than the CPU register but much larger in size.
Computer system
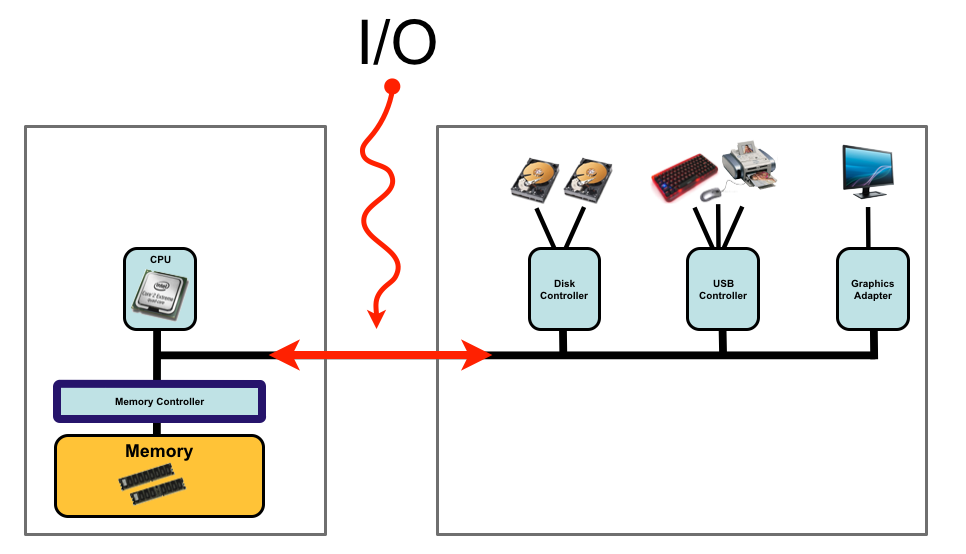
A typical computer system consists of a CPU, memory and external devices such as hard drives (disks), keyboard, screens, mouse and printers. The CPU and the device controllers can execute in parallel, competing for memory cycles. To ensure orderly access to the shared memory, a memory controller is provided whose function is to synchronize the access to the memory.
Input/Output (I/O)
In computing, input/output or I/O (or, informally, io or IO) is the communication between an information processing system, such as a computer, and the outside world, possibly a human or another information processing system. Inputs are the signals or data received by the system and outputs are the signals or data sent from it. The term can also be used as part of an action; to “perform I/O” is to perform an input or output operation. 4
For our purposes, any transfer of information between the CPU/Memory and any of the external devices is considered I/O.
Usually I/O operations does not make use of the CPU but are handled by the external devices.
Operating system
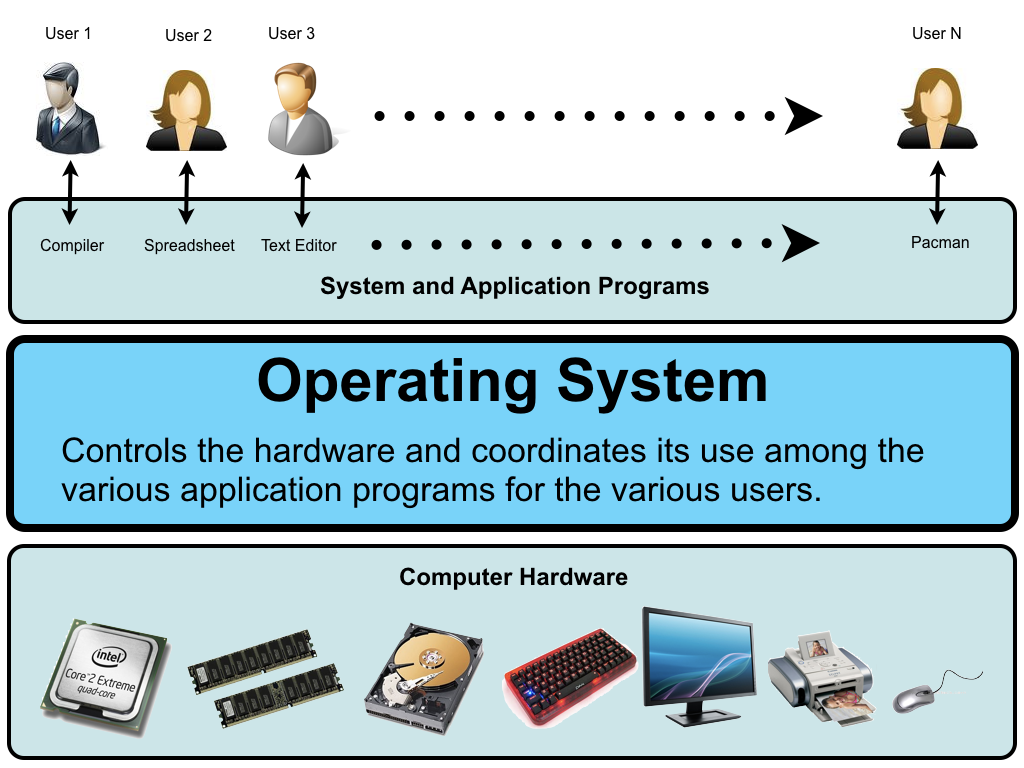
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources and provides common services for computer programs. 5 The OS controls the hardware and coordinates its use among the various application programs for the various user.
Program, executable and process
In order to execute a program, the operating system must first create a process and make the process execute the program.
- Program
- A set of instructions which is in human readable format. A passive entity stored on secondary storage.
- Executable
- A compiled form of a program including machine instructions and static data that a computer can load and execute. A passive entity stored on secondary storage.
- Process
- An executable loaded into memory and executing or waiting. A process typically executes for only a short time before it either finishes or needs to perform I/O (waiting). A process is an active entity and needs resources such as CPU time, memory etc to execute.
CPU context (CPU state)
At any point in time, the values of all the registers in the CPU defines the CPU context. Sometimes CPU state is used instead of CPU context.
More generally, a task context is the minimal set of data used by a task (which may be a process or thread) that must be saved to allow a task to be interrupted, and later continued from the same point. 6
Kernel
The kernel is a computer program that is the core of a computer’s operating system, with complete control over everything in the system. 7
Dual mode operation
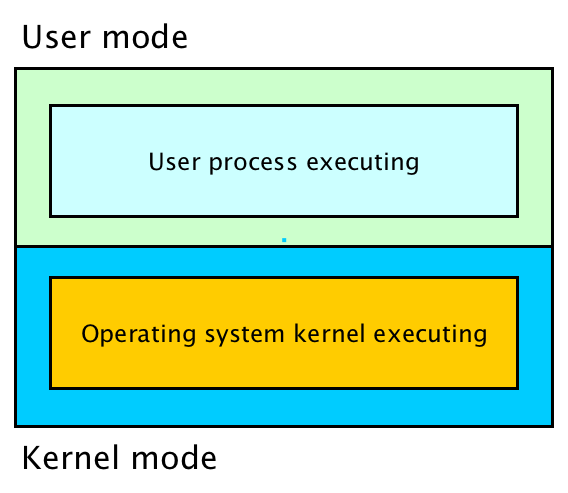
In order to protect the operating system from user processes two modes are provided by the hardware: user mode and kernel mode.
Dual mode operation place restrictions on the type and scope of operations that can be executed by the CPU. This design allows the operating system kernel to execute with more privileges than user application processes.
Synchronous and asynchronous events
Synchronous means happening, existing, or arising at precisely the same time. 8 Asynchronous simply means “not synchronous”.
If an event occurs at the same instruction every time the program is executed with the same data and memory allocation, the event is synchronous. An synchronous event is directly related to the instruction currently being executed by the CPU. On the other hand, an asynchronous event is not directly related to the instruction currently being executed by the CPU.
Exceptions and interrupts
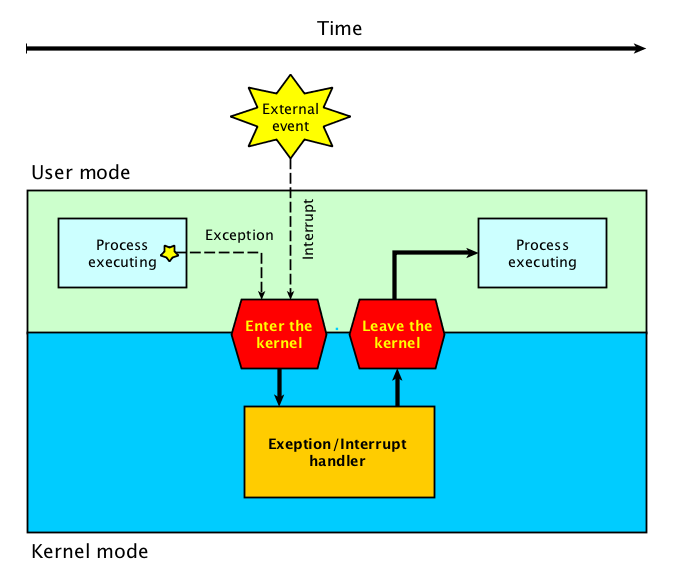
Interrupts and exceptions are used to notify the CPU of events that needs immediate attention during program execution.
Exceptions and interrupts are events that alters the normal sequence of instructions executed by a processor. Such events correspond to electrical signals generated by hardware circuits both inside and outside the CPU chip.
Exceptions are internal and synchronous
- Exceptions are used to handle internal program errors.
- Overflow, division by zero and bad data address are examples of internal errors in a program.
- Another name for exception is trap. A trap (or exception) is a software generated interrupt.
- Exceptions are produced by the CPU control unit while executing instructions and are considered to be synchronous because the control unit issues them only after terminating the execution of an instruction.
Interrupts are external and asynchronous
- Interrupts are used to notify the CPU of external events.
- Interrupts are generated by hardware devices outside the CPU at arbitrary times with respect to the CPU clock signals and are therefore considered to be asynchronous.
- Key-presses on a keyboard might happen at any time. Even if a program is run multiple times with the same input data, the timing of the key presses will most likely vary.
- Read and write requests to disk is similar to key presses. The disk controller is external to the executing process and the timing of a disk operation might vary even if the same program is executed several times.
Exception and interrupt handler
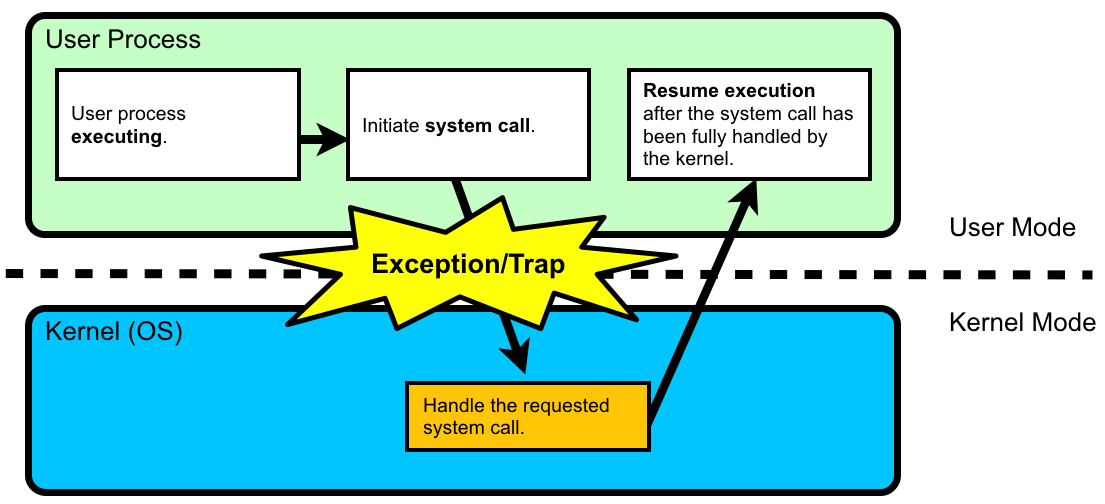
When an exception or interrupt occurs, execution transition from user mode to kernel mode where the exception or interrupt is handled. When the exception or interrupt has been handled execution resumes in user space.
System call
A user program requests service from the operating system using system calls. System calls are implemented using a special system call exception. Another name for exception is trap.